Analysis of Powder Coating on Automotive Micro motor Rotors
Author: Zhou Baowei, Zheng Taishan Guangdong Machinery Research Institute
Abstract: Powder electrostatic coating, as a traditional technology, although originated early, is still in its early stages of large-scale application in the field of rotor insulation for small motor vehicles in China. Currently, most foreign-funded small motor production enterprises in China adopt this technology, which is limited by the increase in cost. In recent years, some of China's more powerful large motor production enterprises have gradually started to use this technology, Domestic professional equipment manufacturers have also begun to refer to German coating technology standards to regulate the production technology of equipment, and have formulated corresponding enterprise standards.
Abstract: Electrical powder coating is a traditional technology Altough it was early, but the motor rotor insulation field of large scale application is still in the initial stage in China
At present, most of small motor manufacturing for foreign companies are using this technology Subject to the increase in cost, some of the powerful and large scale automobile motor manufacturers Began to gradually use this technology at recent years in China
Domestic professional equipment manufacturers have been referred to standard coating technology of Germany for equipment manufacturing technology, and formulate corresponding enterprise standards
Keywords: rotor, insulation, powder electrostatic coating, cmk, fusa
Keywords: rotor, insulation, electrostatic powder coating, CMK, FUSA
Introduction
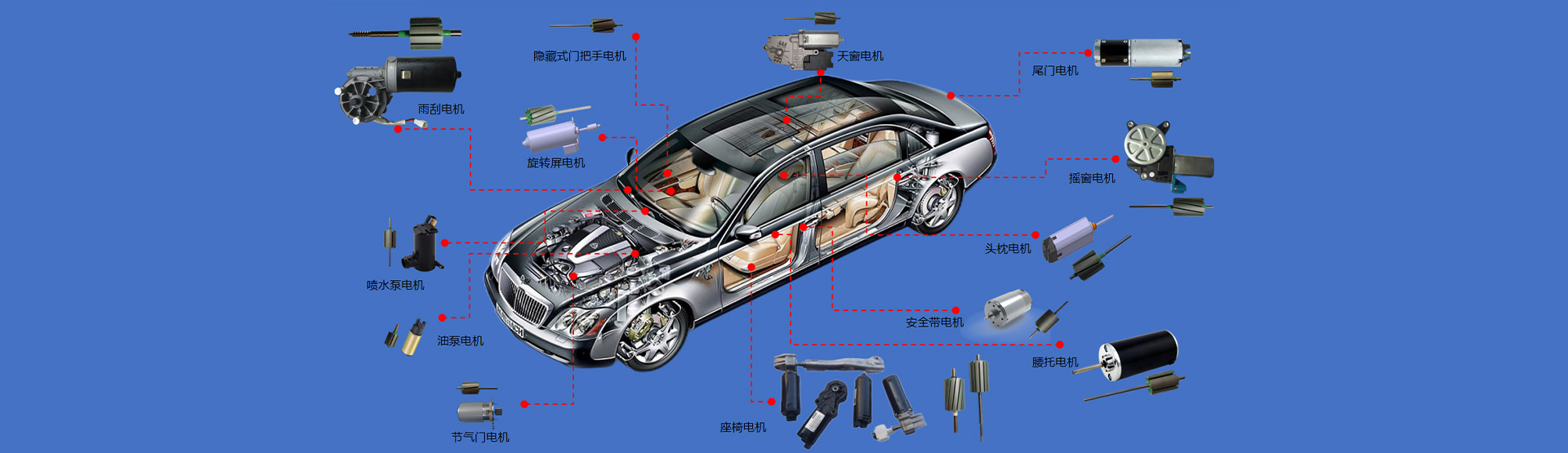
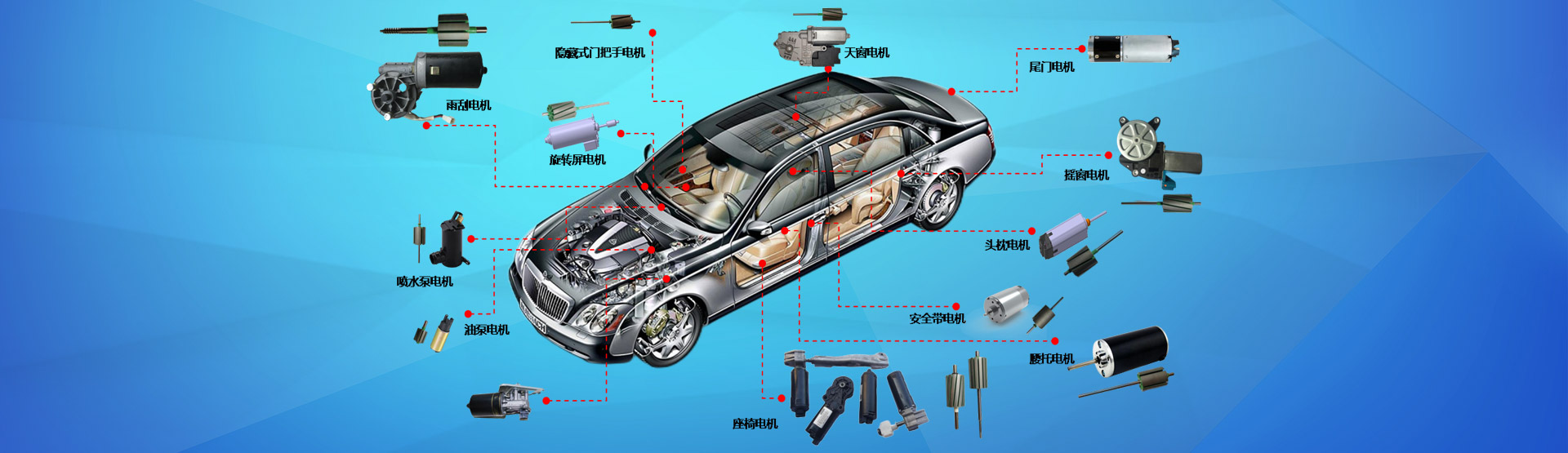
In recent years, China's automobile manufacturing industry has experienced rapid development, with a total number of cars reaching 130 million, with an average of 10 people owning one car. According to the standard of having one car per household in a moderately prosperous life, the current number of cars in China needs to be at least doubled, reaching 400 million. It can be foreseen that with the promotion of urbanization and the trend of urbanization with a large population in China, as well as the construction of new rural areas, the demand for urban and rural automobiles will continue to increase. In addition, with the rapid development of industries such as household appliances, motorcycle appliances, electric tools, electric toys, and automotive appliances, the demand for micro special motors in society will be increasing, with higher quality requirements and wider applications. In the production process of micro special motors, The insulation of motor rotor end faces and wire troughs is a very important task. The insulation process is also becoming increasingly mature and reliable. Major domestic and foreign automobile small motor manufacturers, such as Bosch Automotive Parts, Shanghai Boze Automotive Parts Co., Ltd., Shanghai Fareo Automotive Electrical System Co., Ltd., and Tianjin Asmo Automotive Micro Motor Co., Ltd., have all adopted the new technology of epoxy powder coating, This greatly improves the reliability and service life of the insulation of small motors.
1. Factors affecting the service life of motors
As is well known, the temperature rise (thermal aging) of motors is one of the important reasons for the decrease in insulation performance (aging of insulation materials) and loosening of insulation components. Therefore, when selecting insulation structures, the heat resistance and thermal conductivity of their insulation materials must be considered simultaneously with insulation properties. Taking electromagnetic wires as an example, as the temperature increases, the outer insulation becomes soft, and their shear strength will be lost. If squeezed by other objects at high temperatures, the insulator may undergo plastic deformation or even expose the conductor under external forces, ultimately leading to a short circuit. When the temperature exceeds the insulation's heat resistance rating for a long time, it will cause insulation degradation and excessive degradation. This is particularly important for micro motors used in automobiles, such as window motors, steering wheel assist motors, wiper motors, seat adjustment motors, and other motors with poor ventilation and heat dissipation conditions.
There are many reasons for the heating of electric motors, such as iron loss, copper loss, and mechanical loss during normal operation, which ultimately turn into heat energy consumption. The hot spots in the insulation structure of electric motors mainly include: heat generated by current passing through the winding, heat generated by medium loss, heat generated by eddy current loss and ferromagnetic loss caused by electromagnetic induction, heat generated by friction, vibration, noise, poor contact caused by deviations during mechanical assembly, and heat generated by poor ventilation causing basic temperature rise, etc. These heating causes can cause problems such as shortened service life of motors and increased maintenance costs, especially for motors in specific locations of automobiles. Therefore, choosing insulation materials and production processes with excellent insulation and heat resistance is one of the methods to solve these problems.
2. Insulation materials and processes
In the manufacturing of all types of motors, the insulation materials, insulation structures, and insulation processes used in designing motor insulation not only involve the selection of electrical parameters, external dimensions, and overall structure layout of the motor, but also relate to the reliability and service life of motor operation. The various technical performance indicators in the insulation structure largely reflect the design and manufacturing level of the motor. With the progress of science and technology and the requirements of the usage environment, higher requirements have been put forward for the reliability of motor insulation. To this end, it is necessary to develop and apply new insulation materials, more reasonable insulation structures, advanced manufacturing processes, and scientific insulation testing methods, in order to meet the requirements of long-term electrical, high temperature, mechanical, and various harsh operating conditions of the motor electrical insulation system.
Micro electric motors for automobiles are often used in enclosed environments without ventilation and heat dissipation due to their low voltage but harsh operating conditions. Manufacturers often design motors with lower power to reduce costs, such as window motors, seat motors, and other short-term operating motors. The power required to drive the load is often several times the output power of the motor, which can cause excessive instantaneous load current of the motor and rapid temperature rise of the body, resulting in a series of problems. Therefore, in order to extend the service life and ensure quality and reliability, new production processes must be adopted in insulation materials and insulation processes.
The insulation materials for small motors have undergone significant changes through the continuous efforts of researchers, and the use of new materials has brought about innovation in the production process of small motors. With the increasing improvement of electrostatic coating technology, mainstream micro motor manufacturers have begun to use epoxy powder in large quantities as insulation material for motor rotors, such as products produced by companies such as Akzo Nobel, American 3M, Sumitomo Chemical, etc. The advantages of this insulation material are stable insulation performance, high temperature resistance, easy use, and the ability to cure various insulation surfaces of the rotor in one go through special processes.
3. The cost and advantages and disadvantages of slot paper technology
At present, many micro electric motor rotor manufacturers are still using insulation paper as the insulation material for rotor winding slots. This material and production process have been used for a considerable period of time. Many small and medium-sized motor manufacturers in China with low annual output are the main users, while world-renowned enterprises such as Bosch Automotive Parts, Shanghai Fareo, Tianjin Asmo, etc. have gradually switched to powder coating technology, The main reason why small and medium-sized motor manufacturers do not use powder coating technology is that the material cost of the slot paper process is relatively low, and the mechanical equipment used is also relatively low. However, this insulation method also has many drawbacks, such as low slot filling rate: the actual output power of the motor cannot meet the design requirements, and the motor temperature rises too high when the load is too large; 2. The waste generated after winding is relatively high: due to the deformation of the slot paper when embedded in the slot, the electromagnetic wire is drawn into the external insulation paper during the winding process, causing the entire rotor to be scrapped. This phenomenon results in an implicit waste rate, and the actual cost of expenditure is several times the value of a single rotor before winding; 3. The lack of insulation protection on the rotor end face reduces the insulation degree between the electromagnetic wire and the rotor body, causing insulation hazards in the motor; 4. Easy to cause winding looseness.
4. Powder coating process for motor rotors
The new process of coating insulation powder on the iron core groove of micro motor rotors for automobiles has developed rapidly due to its characteristics of large production volume, high efficiency, and stable process performance. The electrostatic powder coating is pinhole free and has good edge coverage. The coating surface is smooth, the powder adhesion is strong, and the toughness is good. The mechanical and electrical properties are similar to those of impregnating paint, and the maximum layer thickness can reach 0.381 millimeters, which is much thicker than impregnating paint, It is an ideal insulation material.
Some world-class enterprises at home and abroad are all using this technology, and currently some small enterprises in China are also trying this technology. Powder electrostatic coating overcomes some drawbacks of the slot paper process, such as the lack of insulation protection on the rotor end face, susceptibility to winding looseness, low slot filling rate, and easy detachment of the winding from the slot paper. The increase in slot filling ratio under the same rotor structure can effectively enhance the output power of the motor; The rotor insulation is integrated and formed in one go, changing the state of insulation treatment on the rotor end face under the slot paper process; Eliminated some waste products generated after rotor winding; The hot charging process of rotor commutator can be achieved by utilizing the inherent performance of powder coating. However, there are also some drawbacks to powder electrostatic coating, such as the higher price of electrostatic coating equipment compared to slot paper production equipment, the demanding usage environment of the equipment, and the need for a good ventilation system. Some domestic manufacturers of electrostatic coating equipment have poor airtightness, unstable performance, and low powder utilization, which restrict the widespread use of electrostatic coating technology.
There are two types of powder electrostatic coating equipment used by domestic micro motor manufacturers in the early stage. One is low-end coating products in China, which occupy the small motor manufacturers in China. This type of equipment has outdated technology, unstable rotor coating quality, low powder utilization rate, high labor intensity of workers, and cannot be matched with assembly lines, but the equipment cost is low; Another type is mainly imported equipment from abroad, which is widely used in some large motor production plants in China. This type of equipment has advanced technology, high degree of automation in assembly line operations, stable equipment performance, excellent sealing performance, and a powder utilization rate of over 90%. However, the price of the equipment is very high, and many domestic motor manufacturers are not using this equipment due to price constraints, which also limits the development of powder coating technology on the other hand.
To solve this problem, Bosch Automotive Parts Changsha Company is seeking localization of equipment. After jointly developing with domestic equipment manufacturers, they have determined the principle of importing core components from abroad and replacing other components with domestic production. In the technical design, the equipment is divided into three working areas: coating area, cleaning area, and curing area.
The coating area (see Figure 1) is the process area for coating powder on workpieces, consisting of a fluidized bed, an electrostatic generator, electrodes, etc. The electrodes are composed of copper plates and discharge needles, and the electrodes are connected to the cathode of the electrostatic generator. When the electrostatic generator is working, there is an electrostatic high voltage of 55KV-90KV at the cathode. At this time, the air around the discharge needle produces corona phenomenon. The compressed air that has been dried is slowly sent into the coating area from the bottom of the fluidized bed, continuously flowing through the discharge needle and carrying charges. These charged air flows into the fluidized bed through a porous and breathable fluidized plate. The charged gas comes into contact with the epoxy resin powder in the fluidized bed and transfers the charge to the epoxy resin powder. At the same time, it is blown up and forms a boiling cloud, and the powder is suspended in the fluidized bed. The workpiece rotor is connected to the anode of the electrostatic generator, which is grounded at the same time. Under the action of the electrostatic field, the charged epoxy resin powder moves towards the upper motor rotor and is adsorbed on the surface of the rotor. The charge carried by it returns to the electrostatic generator through the anode, completing the powder feeding work of the epoxy resin powder fluidized bed.
The cleaning area is equipped with a powder scraping mechanism and a powder blowing mechanism. When the screw rotates to drive the workpiece rotor into this area, the workpiece is supported and rotated by the rotating mechanism. The powder on the outer diameter surface of the workpiece, which does not need to be coated, is scraped off by the inclined scraper of the powder scraping mechanism. The remaining powder on the protective shaft sleeve will be blown off by the air brush of the upper powder blowing mechanism through compressed air, thus completing the cleaning work of the workpiece rotor.
The solidification zone solidifies the powder on the workpiece rotor through high-frequency induction heating. High frequency heating utilizes the skin heating effect to generate eddy currents on the surface of the workpiece, thereby rapidly heating the surface of the workpiece. The powder adsorbed on the surface is continuously melted, leveled, and gelatinized, and finally solidified to form a uniform hardened insulation coating.
The rotor of the workpiece coated by the coating machine:
Car door and window motor rotor (outer diameter 24mm), car seat motor rotor (outer diameter 28mm),
Car wiper motor rotor (outer diameter 40mm), car steering assist motor rotor (outer diameter 54mm)
After 2 years of trial production, a series of problems such as the uniform stability of electrostatic feeding and the wear resistance of the rotor surface scraping mechanism have been solved. Now, this type of equipment has a short production cycle, a significant decrease in price, stable quality, and a higher utilization rate of epoxy powder than foreign equipment. After testing, the long-term capacity index Cmk ≥ 1.67 and fusa ≥ 98% of the equipment. Currently, 80% of Bosch Automotive Parts Changsha's electrostatic coating equipment is provided by domestic manufacturers. Ultimately, Bosch Automotive Parts will replace all imported equipment with domestic equipment in its domestic rotor production line and prepare to export to factories in Europe and America.
5. Conclusion:
The epoxy powder adopts an electrostatic fluidized bed hot melt coating process to achieve powder electrostatic coating insulation for automotive micro motor rotors and other household electrical motor components, replacing the traditional polyester film composite insulation process. This can reduce the thickness of the insulation layer and improve the slot filling rate by about 10%, providing a prerequisite for large-scale production of coating components. In addition, this technology can also be applied to power electronic devices and chemical pipeline containers and valves, With the continuous development of technology and the continuous updating of powder coating varieties, the continuous improvement of powder electrostatic fluidized bed hot solution coating process equipment, and the integration of computer intelligent control, this process will play a greater role in industrial automation production lines.
Navigation
Contact Us
- Tel:0574-62092593
Fax:0574-62093601
Mb:13958345900
Email:sunta@shunyangelec.com
Add:No. 66, Zhenhai Village, Xiaocao'e Town, Yuyao City, Ningbo City
Analysis of Powder Coating on Automotive Small Motor Rotors
View:522 Release Date:2023/12/1 17:09:45